86% das emissões de dióxido de carbono no Brasil são resultado da queima de combustíveis fósseis para a produção de energia e materiais, segundo o jornal O Globo (2021). Em resposta a essa realidade, 27% das indústrias do país já assumiram compromisso com a neutralidade do carbono, com metas de redução de emissão desse gás. Além dessa mudança de atitude ser benéfica para a questão climática global, ela contribui para o aumento da produtividade, da qualidade de produtos e garante que as indústrias estejam adequadas às regulamentações governamentais exigidas.
Uma indústria de manufatura utiliza gases em variadas etapas do processo produtivo, principalmente na operação de caldeiras. Esse tipo de equipamento transforma a energia do combustível em energia térmica, aquecendo a água depositada em seus tanques e produzindo vapor. Alguns dos processos industriais mais comuns para a utilização de vapor são o aquecimento direto e indireto, a pasteurização, a esterilização e o processo de secagem. Para suprir a demanda existem diferentes tipos de caldeiras industriais, como:
- Flamotubulares: São caracterizadas por uma configuração em que os gases emitidos passam por dentro dos tubos, enquanto a água fica em tubulões. Elas são ideias para geração de vapor de até 30 ton/h, e conhecidas pela sua rápida adaptabilidade a mudanças de demanda de vapor. Também, conseguem utilizar diversos tipos de combustíveis, incluindo a biomassa;
- Aquatubulares: Nesse caso, a água circula na parte interna dos tubos, enquanto os gases resultantes da combustão ficam do lado externo. A indústria a utiliza para a geração de energia elétrica, pela sua capacidade de suportar alta pressão e gerar altas quantidades de vapor.
- Recuperação de calor: São projetadas para aproveitar o calor residual de processos industriais, como turbinas, motores e fornos. Esse calor gera vapor, que pode ser aplicado no aquecimento industrial, por exemplo.
Caminho do vapor em Processos Industriais
A escolha de qual combustível será utilizado é um dos fatores que mais impacta na emissão de gases. Combustíveis renováveis, como biomassa, biogás, óleos vegetais e resíduos industriais, são alternativas sustentáveis para a queima em caldeiras industriais. Eles ajudam a reduzir as emissões de dióxido de carbono e promovem a sustentabilidade, além de serem frequentemente mais econômicos e acessíveis.
Por mais que perdas de eficiência durante a distribuição do vapor, ou processos subsequentes específicos possam causar a emissão de gases, a geração de vapor em caldeiras é o seu maior responsável. Para que o vapor cumpra seu objetivo, ele passa pelo menos pelas seguintes etapas:
- Geração de Vapor na Caldeira: O processo começa com a caldeira, onde combustíveis (fósseis ou renováveis) são queimados para aquecer a água. A água aquecida se transforma em vapor.
- Distribuição do Vapor: O vapor gerado é então distribuído através de uma rede de tubulações. Essas tubulações são projetadas para manter a pressão e a temperatura do vapor, garantindo que ele chegue aos pontos de uso com eficiência.
- Controle e Regulagem: Antes de chegar aos processos específicos, o vapor passa por válvulas de controle e regulagem que ajustam sua pressão e temperatura conforme necessário para cada aplicação.
- Utilização em Processos Industriais:
- Aquecimento Direto e Indireto: O vapor é utilizado para aquecer materiais diretamente ou através de trocadores de calor.
- Pasteurização e Esterilização: Na indústria de alimentos e bebidas, o vapor é usado para pasteurizar e esterilizar produtos, garantindo sua segurança e qualidade.
- Movimentação de Turbinas: Em usinas de energia, o vapor movimenta turbinas para gerar eletricidade.
- Secagem: O vapor é utilizado para secar materiais, como madeira e papel, garantindo a qualidade do produto final.
- Limpeza: Em lavanderias industriais e outras aplicações, o vapor é usado para limpeza profunda e eficiente.
- Condensação e Retorno: Após ser utilizado, o vapor se condensa e retorna ao estado líquido. Esse condensado pode ser reciclado e enviado de volta à caldeira para ser aquecido novamente, fechando o ciclo e aumentando a eficiência energética.
Tipos de Gases no Processo de criação de vapor em uma Caldeira Industrial
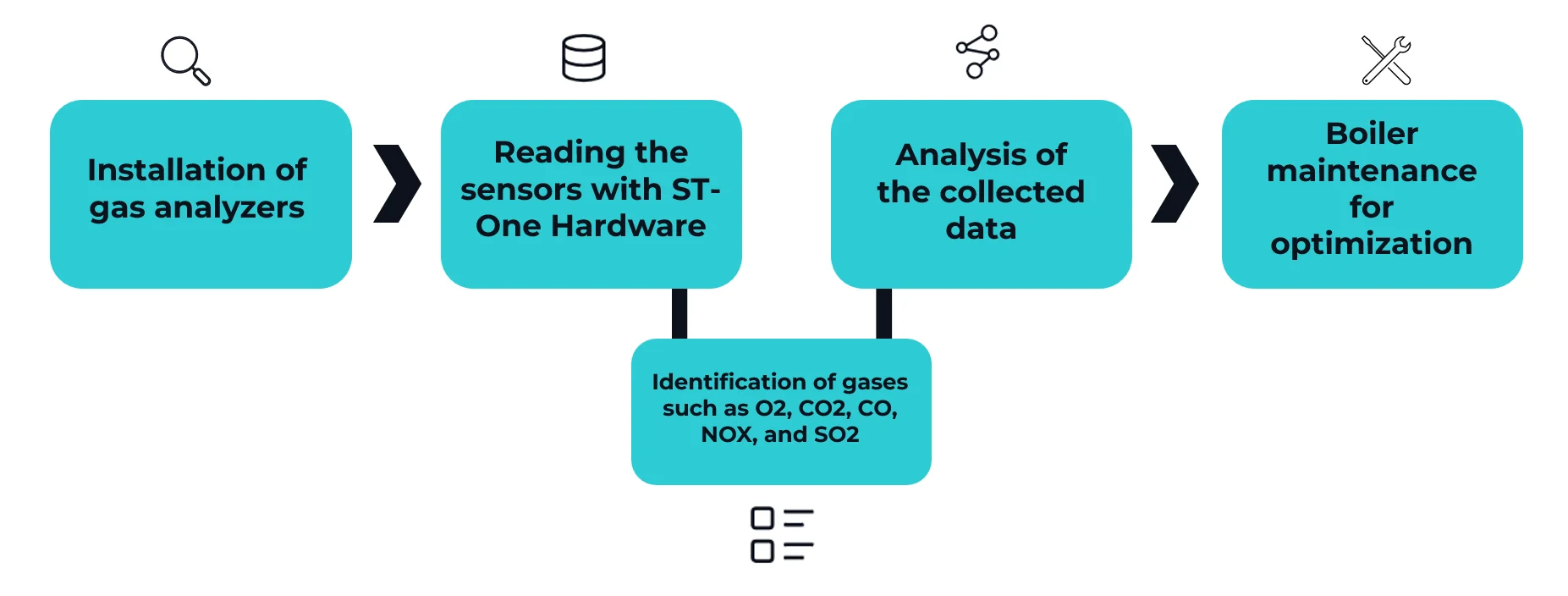
Devido a influência tanto na produtividade quanto na qualidade do produto, é preciso medir os tipos de gases emitidos. O primeiro passo é a instalação de analisadores de gás, sendo os de infravermelho (IR) e espectrometria de massa (SM) os mais usados. Na sequência, se faz necessário o uso de tecnologias que fazem a leitura desses sensores, e armazenam as informações coletadas em um banco de dados. Medindo a composição dos gases, em tempo real, é possível explorar a análise de dados e ter novos insights para melhorar a performance das caldeiras. O último passo é realizar ajustes necessários nas caldeiras.
Cada tipo de gás indica algo sobre o processo produtivo. Nível inadequados de oxigênio (O2) ajudam a determinar se há excesso ou falta de ar na combustão ou problemas na mistura de combustível-ar. Já o dióxido de carbono (CO2) está relacionado à quantidade de combustível queimado, níveis altos desse gás indicam que a queima foi completa. O monóxido de carbono (CO) indica a eficiência da produção, pois esse é um subproduto perigoso proveniente combustão incompleta. O óxido de nitrogênio (NOX) é um poluente significativo, portanto sua medição é importante para avaliar o impacto ambiental. Por último, o dióxido de enxofre (SO2) é relevante em caldeiras que utilizam combustíveis fósseis, sua alta presença indica uso de combustível de baixa qualidade.
O Potencial de Aquecimento Global (PAG) possui critérios para medir o impacto de cada gás de efeito estufa. Ele compara a capacidade de retenção de calor de um gás com o dióxido de carbono por um período específico. Nas indústrias, isso se enquadra em três categorias: Escopo 1 (produzidas diretamente pela empresa), Escopo 2 (gerado pela energia e demais recursos), Escopo 3 (resultantes de fontes indiretas na cadeia de suprimentos).
Criação de Vapor: Eficiência em Caldeiras Industriais
A coleta de dados focada na emissão de gases em uma caldeira permite variados tipos de análise, essenciais para garantir a eficiência energética, a conformidade regulatória e a sustentabilidade ambiental. Entre as principais análises estão a de gases de exaustão mede poluentes como CO₂, CO, NOₓ e SO₂, identificando problemas na combustão e necessidade de manutenção. A de combustão, que monitora a eficiência e a presença de gases poluentes, permitindo ajustes na relação ar-combustível e temperatura da chama. E a termografia detecta pontos quentes, indicando problemas de isolamento e ineficiências na transferência de calor.
Além destas análises direcionadas, a análise de eficiência de caldeira é essencial. Para realizar esta análise é primeiro necessário entender o como é calculada: existem dois métodos principais: o método direto e o método indireto (ou método de perdas).
Método Direto
O método direto calcula a eficiência da caldeira com base na relação entre a energia útil gerada e a energia fornecida pelo combustível. A fórmula é:
Eficiência (%)= (Q×(H−h) / q×GCV)×100
Onde:
- Q = Saída de calor em kJ
- H = Entalpia do vapor em kJ/kg
- h = Entalpia da água de alimentação em kJ/kg
- q = Entrada de combustível em kg
- GCV = Valor Calorífico Bruto do combustível em kJ/kg
Método Indireto (ou Método de Perdas)
O método indireto calcula a eficiência da caldeira considerando as perdas de energia. As principais perdas incluem:
- Perdas de calor nos gases de combustão
- Perdas de calor devido à umidade no combustível
- Perdas de calor devido à umidade no ar de combustão
- Perdas de calor devido à radiação e convecção
A fórmula geral para o método indireto é: Eficiência (%)=100−Perdas Totais(%)
Indicadores de Desempenho para o cálculo de Eficiência em Caldeiras Industriais
A análise de desempenho de sistemas de geração de vapor envolve diversos fatores que impactam diretamente na eficiência, segurança e sustentabilidade do processo. Um dos principais indicadores é a relação entre o vapor produzido e o volume de combustível consumido, que permite avaliar a quantidade de vapor gerada por unidade de combustível, refletindo diretamente a eficiência do sistema. A temperatura da água de alimentação também é fundamental, pois quanto mais quente estiver essa água, menor será a energia necessária para transformá-la em vapor, contribuindo para uma operação mais eficiente. Outro aspecto relevante é o poder calorífico do combustível, já que combustíveis com maior capacidade de liberação de energia por unidade de massa são naturalmente mais eficientes.
Além disso, a vazão dos gases de exaustão deve ser cuidadosamente monitorada, pois vazões excessivas podem indicar perdas de calor significativas, reduzindo o rendimento global do sistema. O isolamento térmico desempenha um papel crucial nesse contexto: um bom isolamento evita perdas de calor por radiação e convecção, mantendo a energia dentro do sistema. A regulagem da queima, por sua vez, deve ser ajustada para garantir a proporção ideal entre ar e combustível, otimizando a combustão e evitando excessos que resultem em perdas ou aumento de poluentes.
Com base nessas análises, é possível extrair informações valiosas para a operação e manutenção do sistema. A otimização da combustão, por exemplo, permite melhorar a relação ar-combustível e controlar a temperatura da chama, resultando em maior eficiência e menor emissão de poluentes.
Impacto da Ciência de Dados na Gestão de Emissões Industriais
Segundo o Boston Consulting Group(2023), o uso da Ciência de Dados tem o potencial de evitar a emissão de 2,6 a 5,3 gigatons de CO2. Em um contexto global, isso representa uma redução de 5% a 10% das emissões previstas pelo Acordo de Paris.
Além disso, ela é uma importante aliada para aspectos relacionado à ESG (Environmental, Social and Governance). Na parte ambiental, além da redução de gases poluentes, age na otimização do uso de recursos naturais, como água e energia. Também, auxilia na implementação de sistemas de logística reversa, facilitando a reutilização de materiais e impactando na redução de custo.
Já no social, o uso dessa tecnologia para redução de poluentes melhora a saúde e a segurança dos colabores e das comunidades próximas às fábricas. Isso demonstra um compromisso com o bem-estar social.
Por último, na governança, o monitoramento de emissões demonstra transparência, o que melhora a reputação da indústria e aumenta a confiança de investidores. Além disso, é capaz de identificar riscos operacionais.
Em suma, a análise de emissão de gases das caldeiras é benéfica para a indústrias de várias formas. A ciência de dados permite identificar os diferentes gases produzidos, e analisar o nível de cada um para descobrir pontos de melhoria na caldeira. A partir disso, a indústria pode agir visando o aumento de produtividade, além de entrar em conformidade com leis de proteção ambiental. Saiba mais sobre a ST-One .