A sigla ESG (Environmental, Social, and Governance) foi usada pela primeira vez em 2005, no relatório “Who Cares Wins” (em português, “Quem se Importa Ganha”). Elaborado pelo Pacto Global da ONU (Organização das Nações Unidas), o conceito vem ganhando espaço na mídia e nos negócios nos últimos anos. Segundo a Fundação Vanzolini, para equilibrar esses três pilares, a indústria deve integrar esse pensamento no core business e na cultura organizacional.
Ações como desenvolver sistemas de logística reversa e definir a destinação de resíduos, priorizando a reciclagem, se enquadram no pilar ambiental (Environmental). No pilar social (Social), é possível investir em qualificação e treinamento dos colaboradores. Por último, a governança (Governance) pode ser aprimorada quando os processos da organização são elaborados de maneira transparente e com uma gestão otimizada.
No Brasil, o estudo “A Maturidade ESG nas Empresas Brasileiras: Avanços e Desafios 2024“, da Beon ESG e Aberje, entrevistou 401 líderes e revelou que 54% das grandes empresas possuem estratégias de sustentabilidade, mas enfrentam desafios em métricas e transparência. Já o relatório “ESG na Indústria Brasileira“, do Pacto Global da ONU, aponta que 78,4% das organizações incorporaram ESG, com destaque para grandes indústrias.
Na América Latina, o estudo “Sustentabilidade na Agenda dos Líderes Latino-Americanos“, da SAP, entrevistou 400 empresas e evidenciou o crescimento acelerado da adoção ESG, com destaque para o Brasil. A Forbes, em “ESG Além das Fronteiras“, discute a importância da sustentabilidade na cadeia de valor, destacando a posição do Brasil como um player crucial na agenda global de sustentabilidade. Na América do Norte, o estudo “Global Manufacturing Prospects 2023“, da KPMG, analisou 182 CEOs e destacou desafios em ESG, retenção de talentos e tecnologia, além das metas de neutralidade de carbono.
Gestão Energética com ISO 50001: Padronização e Eficiência
A ISO 50001 é uma ferramenta de gestão voltada para o controle de energia, servindo como um instrumento essencial para a padronização da gestão energética. Ela pode ser implementada em indústrias de diferentes níveis de maturidade, que utilizam variadas fontes de energia, desde elétrica até gás. Suas diretrizes foram incorporadas ao Plano Nacional de Eficiência Energética (PNEf) e ao Plano Nacional de Energia 2030, como mecanismos para economia de consumo.
No Brasil, a ISO 50001 é representada pela ABNT e sua aplicação nas indústrias segue um processo estruturado, que inclui:
- Análise do contexto: Entender as necessidades e expectativas das partes interessadas, determinar o escopo e a estrutura do Sistema de Gestão de Energia (SGE).
- Compromisso com a liderança: Definir a política energética, responsabilidades e autoridades.
- Estabelecimento de metas energéticas: Planejamento para atingir essas metas.
- Gestão do uso e consumo de energia: Implementação de sistemas, comunicação e documentação.
Para atingir as metas definidas, a ISO 50001 foca na busca pela melhoria contínua, utilizando duas ferramentas básicas: o ciclo PDCA da área de qualidade e o nível de consumo energético da área de termodinâmica. A figura abaixo ilustra como funciona esse processo.
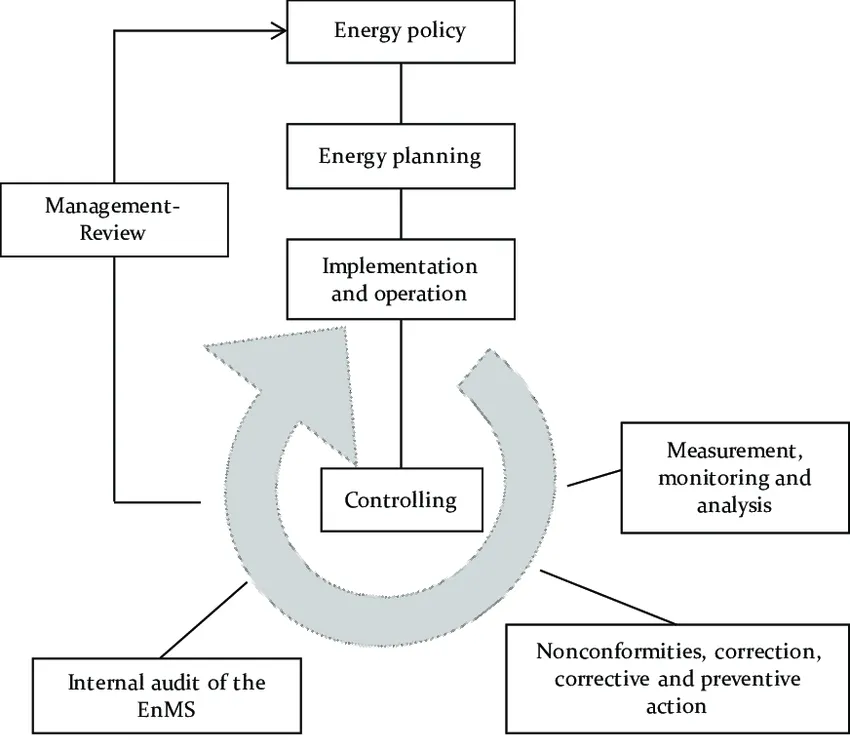
Qualquer organização, independentemente do seu domínio de gestão de energia, pode implementar a ISO 50001 para estabelecer uma linha de base e melhorar em um ritmo adequado. Isso é feito independentemente do contexto, o que significa que não há metas absolutas de desempenho energético além daquelas estabelecidas na política energética da indústria e da conformidade com requisitos legais. Assim, duas organizações realizando operações semelhantes, mas com desempenhos energéticos distintos, podem ambas estar em conformidade com seus requisitos (ABNT NBR ISO 50001, 2011).
ESG: Sustentabilidade que Gera Resultados
De acordo com o Bureau Veritas (2020), uma empresa francesa especializada em testes de inspeção, a certificação ISO 50001 pode melhorar o desempenho energético em até 30%. Além disso, a mesma instituição estima que a norma impacte positivamente 60% do consumo total de energia mundial. Esses benefícios incentivaram o Governo Brasileiro a criar diversos programas e iniciativas voltados para a eficiência energética e a sustentabilidade.
O Programa de Eficiência Energética (PEE) visa promover o uso eficiente de energia elétrica através da adoção de tecnologias e práticas diversas no cotidiano. Focado na indústria, temos o Programa Brasileiro de Etiquetagem (PBE), que classifica produtos quanto à eficiência energética, e o Programa de Conservação de Eletricidade (Procel).
Essas ações incentivam a indústria a produzir e os consumidores a escolher produtos mais eficientes, que consomem menos energia. Segundo a Sebrae (2023), as ações do Procel, ao etiquetar produtos que utilizam eletricidade, resultaram em uma economia de 23 TWh, o que representa 4,87% do consumo de energia elétrica em 2018.
Além dos ganhos financeiros e ambientais, o uso eficiente de energia também impacta outras áreas. A ONG American Council for an Energy-Efficient Economy (2022) mostra que uma redução de 15% no consumo anual de energia resultaria em 2.190 vidas salvas. Esses dados reforçam que os programas trazem muitos resultados positivos, impactando todo o ambiente de forma significativa.
Ciência de Dados: Pilar do Desenvolvimento Sustentável
A implementação de normas e programas como a ISO 50001 reduz a emissão de gases de efeito estufa, diminui os custos energéticos e mitiga outros impactos ambientais associados à gestão de energia. Além disso, a ISO 50001 promove a transparência organizacional e facilita a comunicação na gestão de recursos energéticos, servindo como base para a avaliação e priorização da aplicação de novas tecnologias eficazes, que permitem a integração com outros sistemas.
Para garantir que a produção esteja alinhada com as metas e objetivos estabelecidos, é essencial que a indústria instale sistemas de monitoramento e medição de indicadores, um pré-requisito da norma. Uma das opções para isso é a implementação de soluções que permitem a coleta e análise de dados. A partir desses dados, é possível compreender melhor os padrões de consumo e auxiliar na tomada de decisões relacionadas ao uso de energia. Essa digitalização também possibilita a revisão da eficácia do ciclo atual, através do histórico disponibilizado, promovendo a melhoria contínua.
Essas tecnologias permitem a integração com outros sistemas, podendo ser utilizadas também no monitoramento de outros recursos, como a água. Por exemplo, o monitoramento inteligente desse recurso em uma indústria de bebidas resultou em um uso mais eficiente e menor desperdício.
Assim como a ISO 50001, a cultura de dados pode ser implementada em indústrias com diferentes níveis de maturidade. Essa norma é apenas um exemplo de como ações de ESG podem ser executadas. Através da digitalização, é possível descobrir e explorar diversas melhorias que contribuem para o desenvolvimento sustentável e elevam a indústria a um novo patamar de produtividade.